Introducing the eco pyramid readworks answer key, a comprehensive guide to unraveling the intricacies of ecological pyramids and their profound significance in ecosystem dynamics. This key unlocks a deeper understanding of the intricate relationships between organisms and their environment, providing valuable insights into the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth.
Ecological pyramids, as depicted in the eco pyramid readworks answer key, serve as visual representations of the energy flow and trophic levels within an ecosystem. They reveal the interconnectedness of species, from producers at the base to top predators at the apex, and illustrate the transfer of energy and biomass through the food web.
The Eco Pyramid

An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation of the biomass or productivity at each trophic level in an ecosystem. It illustrates the flow of energy and matter through the ecosystem, with producers at the base and top predators at the apex.
There are three main types of ecological pyramids:
Pyramid of Numbers
A pyramid of numbers represents the number of individual organisms at each trophic level. Typically, the base of the pyramid is wide, representing a large number of producers, while the apex is narrow, representing a small number of top predators.
Pyramid of Biomass
A pyramid of biomass represents the total mass of living organisms at each trophic level. It is similar to a pyramid of numbers, but takes into account the size and weight of organisms. Pyramids of biomass are often used to compare different ecosystems or to track changes in biomass over time.
Pyramid of Energy
A pyramid of energy represents the amount of energy that flows through each trophic level. It is typically expressed in units of calories or joules. Pyramids of energy are used to track the efficiency of energy transfer through an ecosystem and to identify areas where energy is lost.
Levels of the Eco Pyramid
An ecological pyramid, also known as a trophic pyramid, depicts the energy flow within an ecosystem. It categorizes organisms based on their trophic levels, which indicate their feeding relationships and the amount of energy they transfer.
There are three main trophic levels within an ecological pyramid:
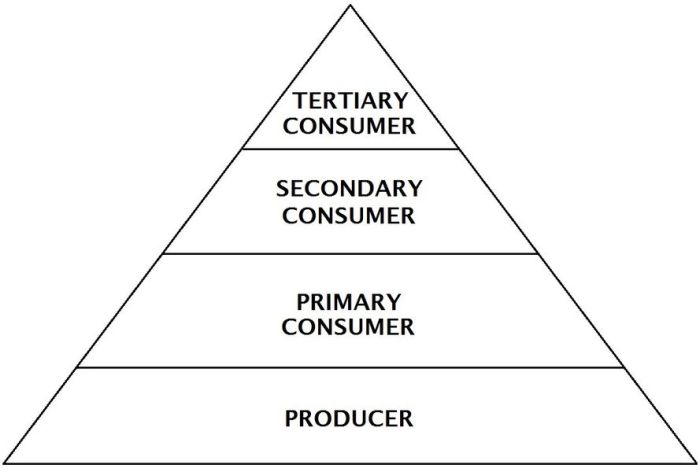
Producers
- Producers, also known as autotrophs, form the base of the pyramid.
- They are organisms that can synthesize their own food using inorganic substances, such as plants and algae, through the process of photosynthesis.
Consumers
- Consumers, also known as heterotrophs, are organisms that cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms to obtain energy.
- They are further classified into different levels based on their feeding habits:
- Primary consumers(herbivores) consume producers directly.
- Secondary consumers(carnivores) consume primary consumers.
- Tertiary consumers(top predators) consume secondary consumers.
Decomposers
- Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organisms and organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem.
- They play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
Energy Flow and Transfer Efficiency
Energy flows through the ecological pyramid from producers to consumers. At each trophic level, only a fraction of the energy is transferred to the next level. This is known as the energy transfer efficiency.
The energy transfer efficiency is typically around 10%, meaning that only about 10% of the energy available at one trophic level is transferred to the next.
This inefficiency results in a pyramid shape, with the producer level having the greatest biomass and the top predator level having the smallest.
Factors Affecting the Eco Pyramid
The shape and stability of ecological pyramids are influenced by various factors. These include:
Environmental Conditions, The eco pyramid readworks answer key
Environmental conditions such as temperature, sunlight, and rainfall can affect the abundance and distribution of organisms at different trophic levels. For instance, in areas with extreme temperatures, there may be fewer primary producers and more decomposers, resulting in a narrower-based pyramid.
Resource Availability
The availability of resources, such as food, water, and shelter, can also influence the shape of the eco pyramid. If resources are scarce, competition among organisms will be intense, leading to a pyramid with a narrow base and a wide apex.
Competition
Competition between organisms for resources can affect the shape of the eco pyramid. When competition is intense, some species may be outcompeted and their populations may decline, resulting in a pyramid with a narrow base and a wide apex.
Ecological Succession
Ecological succession is the gradual change in the composition of a community over time. As a community progresses through different stages of succession, the shape of the eco pyramid may change. For example, in early stages of succession, there may be a large number of primary producers and a small number of consumers, resulting in a pyramid with a wide base and a narrow apex.
As succession progresses, the number of consumers may increase, leading to a pyramid with a narrower base and a wider apex.
Importance of the Eco Pyramid
Ecological pyramids play a crucial role in comprehending the intricate dynamics and biodiversity within ecosystems. They provide a visual representation of the trophic levels and energy flow, offering insights into the structure and functioning of ecological communities.The eco pyramid highlights the interconnectedness of species within an ecosystem.
It demonstrates how energy is transferred from primary producers to top predators, and how each trophic level relies on the one below it for sustenance. This understanding is essential for assessing the stability and resilience of ecosystems, as well as predicting the potential impacts of environmental changes.
Implications of Human Activities on the Eco Pyramid
Human activities can significantly impact the eco pyramid, leading to imbalances and potential ecosystem collapse. Overexploitation of resources, such as excessive fishing or deforestation, can reduce the abundance of primary producers and disrupt the energy flow throughout the pyramid. Pollution and climate change can also affect the availability of resources and alter the relationships between species, leading to shifts in trophic levels and biodiversity loss.Understanding
the implications of human activities on the eco pyramid is crucial for developing sustainable practices that minimize ecosystem degradation and preserve biodiversity. By considering the potential consequences of our actions, we can make informed decisions that promote ecosystem health and ensure the long-term sustainability of our planet.
Case Studies: The Eco Pyramid Readworks Answer Key

Ecological pyramids have been widely used to analyze and understand ecosystem dynamics in real-world scenarios. These case studies provide valuable insights into the structure and functioning of various ecosystems.
Pyramid of Energy in a Grassland Ecosystem
In a grassland ecosystem, the pyramid of energy depicts the flow of energy from producers to consumers. Producers, such as grasses and other plants, convert sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis. This energy is then passed on to primary consumers, such as grasshoppers and mice, which feed on the plants.
Secondary consumers, such as snakes and birds, feed on the primary consumers. Tertiary consumers, such as hawks and coyotes, feed on the secondary consumers. Each level of the pyramid represents a decrease in the amount of energy available to the next level due to energy loss during transfer and metabolic processes.
Data from a study conducted in a Kansas grassland showed that the pyramid of energy had a distinct shape. The producers had the highest energy content, followed by the primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers. The pyramid shape reflects the decrease in energy availability at each trophic level, highlighting the importance of energy conservation in ecosystems.
Pyramid of Biomass in a Forest Ecosystem
The pyramid of biomass represents the total mass of living organisms at each trophic level. In a forest ecosystem, trees and other plants form the base of the pyramid as producers. Herbivores, such as deer and rabbits, feed on the plants and constitute the primary consumer level.
Carnivores, such as wolves and bears, feed on the herbivores and form the secondary consumer level. Apex predators, such as eagles and lions, feed on the carnivores and occupy the tertiary consumer level.
A study in a temperate forest in North America revealed that the pyramid of biomass had a distinct shape. The producers had the highest biomass, followed by the primary consumers, secondary consumers, and apex predators. The shape of the pyramid indicates that the total mass of organisms decreases at each higher trophic level, reflecting the loss of biomass due to energy transfer and metabolic processes.
Pyramid of Numbers in an Aquatic Ecosystem
The pyramid of numbers represents the number of individual organisms at each trophic level. In an aquatic ecosystem, phytoplankton, such as algae, form the base of the pyramid as producers. Zooplankton, such as small crustaceans, feed on the phytoplankton and constitute the primary consumer level.
Fish, such as herring and sardines, feed on the zooplankton and form the secondary consumer level. Larger predators, such as sharks and dolphins, feed on the fish and occupy the tertiary consumer level.
Data from a study conducted in the North Atlantic Ocean showed that the pyramid of numbers had a distinct shape. The producers had the highest number of individuals, followed by the primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers. The shape of the pyramid indicates that the number of organisms decreases at each higher trophic level, reflecting the limited resources available and the competitive interactions among organisms.
FAQ Section
What is an ecological pyramid?
An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation of the trophic levels within an ecosystem, depicting the flow of energy and biomass from producers to consumers.
What are the different types of ecological pyramids?
There are three main types of ecological pyramids: pyramid of numbers, pyramid of biomass, and pyramid of energy.
How do ecological pyramids help us understand ecosystem dynamics?
Ecological pyramids provide insights into the energy flow, trophic relationships, and stability of ecosystems, helping us understand how species interact and how ecosystems respond to environmental changes.