Which of the following statements about gerrymandering is true? Gerrymandering is the practice of redrawing electoral district boundaries to give one political party an unfair advantage over its opponents. It is a controversial practice that has been used for centuries, and it continues to be a major issue in American politics today.
There are many different types of gerrymandering, but they all share the common goal of giving one party an unfair advantage. Some of the most common types of gerrymandering include:
Definition and Explanation of Gerrymandering: Which Of The Following Statements About Gerrymandering Is True
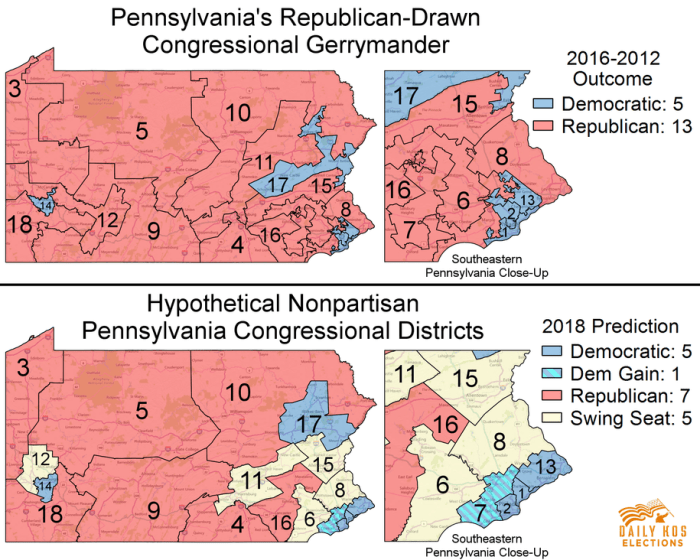
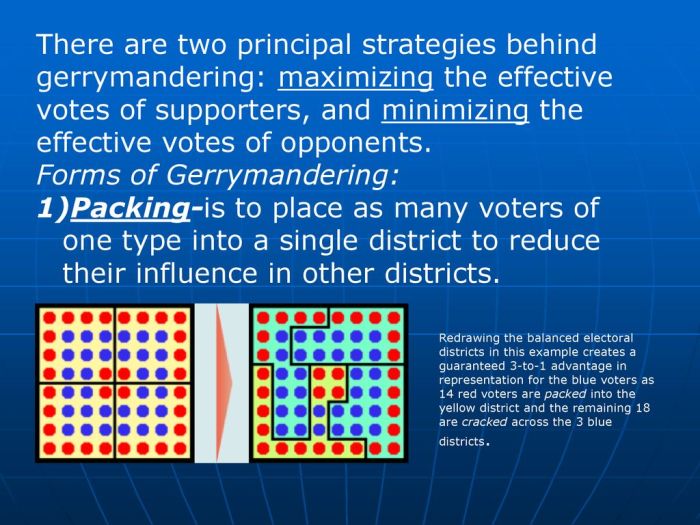
Gerrymandering refers to the manipulation of electoral boundaries to favor a particular political party or group. Its purpose is to create an unfair advantage in elections by intentionally drawing district lines to concentrate or disperse voters of specific affiliations. Gerrymandering can be implemented through various methods, including:
- Packing:Concentrating voters of one party into a single district to minimize their influence in other districts.
- Cracking:Dividing voters of one party into multiple districts to dilute their voting power.
- Stacking:Creating a district with an overwhelming majority of voters from one party to ensure its electoral dominance.
Types of Gerrymandering
Gerrymandering can be categorized into several types, each with distinct characteristics and strategies:
- Partisan Gerrymandering:Manipulating district lines to benefit a particular political party.
- Racial Gerrymandering:Drawing district lines to concentrate or disperse racial or ethnic minority voters to influence electoral outcomes.
- Incumbent Protection:Designing districts to protect incumbents from electoral challenges.
- Bipartisan Gerrymandering:Creating districts that favor both major political parties to prevent competitive elections.
Impact of Gerrymandering
Gerrymandering has significant political and social consequences:
- Distorted Representation:Gerrymandered districts can result in legislatures that do not accurately reflect the preferences of the electorate.
- Reduced Voting Rights:Gerrymandering can disenfranchise certain groups of voters by diluting their influence or making it more difficult for them to elect candidates of their choice.
- Political Polarization:Gerrymandering can exacerbate political polarization by creating safe districts where extreme views are reinforced.
- Diminished Electoral Competition:Gerrymandering can reduce competition in elections, leading to uncontested races or outcomes that are predetermined.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Gerrymandering has faced legal challenges and ethical concerns:
- Legal Challenges:Gerrymandering has been challenged in courts, with some cases reaching the Supreme Court. The legal basis for these challenges often involves violations of the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment.
- Ethical Concerns:Gerrymandering raises ethical concerns about fairness, democracy, and the integrity of elections. It can undermine the principle of “one person, one vote” and create a system where the outcome of elections is predetermined rather than based on the will of the electorate.
Strategies to Address Gerrymandering, Which of the following statements about gerrymandering is true
Efforts to address gerrymandering include:
- Independent Redistricting Commissions:Creating independent bodies to draw district lines, removing the influence of partisan interests.
- Proportional Representation:Implementing electoral systems that allocate seats based on the proportion of votes received, rather than geographic districts.
- Multi-Member Districts:Creating districts that elect multiple representatives, increasing the likelihood of minority representation.
- Ranked-Choice Voting:Allowing voters to rank candidates in order of preference, which can help reduce the impact of gerrymandering.
FAQ Insights
What is gerrymandering?
Gerrymandering is the practice of redrawing electoral district boundaries to give one political party an unfair advantage over its opponents.
Why is gerrymandering a problem?
Gerrymandering is a problem because it undermines the integrity of our democracy. It makes it more difficult for voters to elect the candidates of their choice, and it gives one party an unfair advantage over its opponents.
What can be done to stop gerrymandering?
There are a number of things that can be done to stop gerrymandering, including:
- Passing laws that create independent redistricting commissions.
- Using nonpartisan criteria to draw district boundaries.
- Educating voters about the problem of gerrymandering.