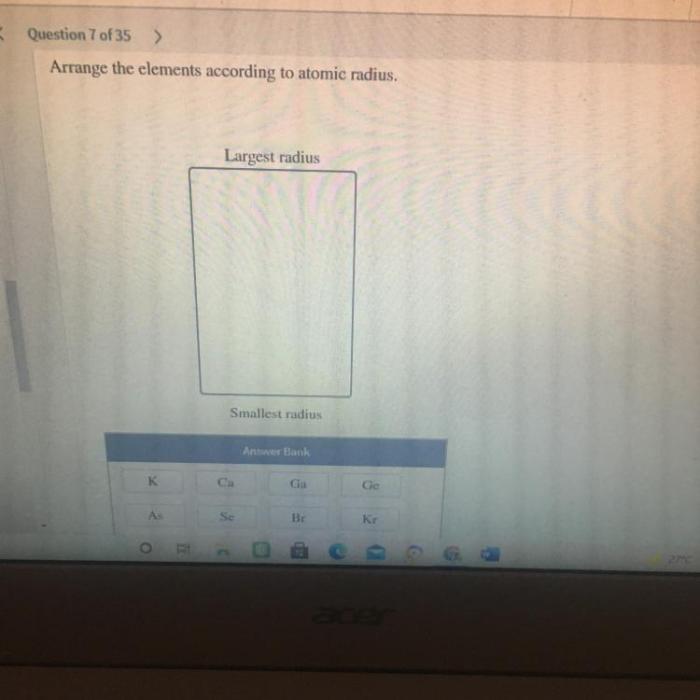
Arrange these elements according to atomic radius embarks on an enlightening odyssey, inviting readers to delve into the captivating world of atomic structure and its profound influence on the periodic table. This comprehensive exploration unveils the intricate relationship between atomic number, electron configuration, and the elusive concept of atomic radius, unraveling the secrets that govern the chemical properties of elements.
As we embark on this atomic adventure, we will uncover the experimental techniques that meticulously measure atomic radius, deciphering the subtle nuances that distinguish one element from another. We will traverse the periodic table, charting the fascinating trends in atomic radius across periods and groups, and unravel the profound implications these trends hold for chemical bonding and reactivity.
Atomic Radius
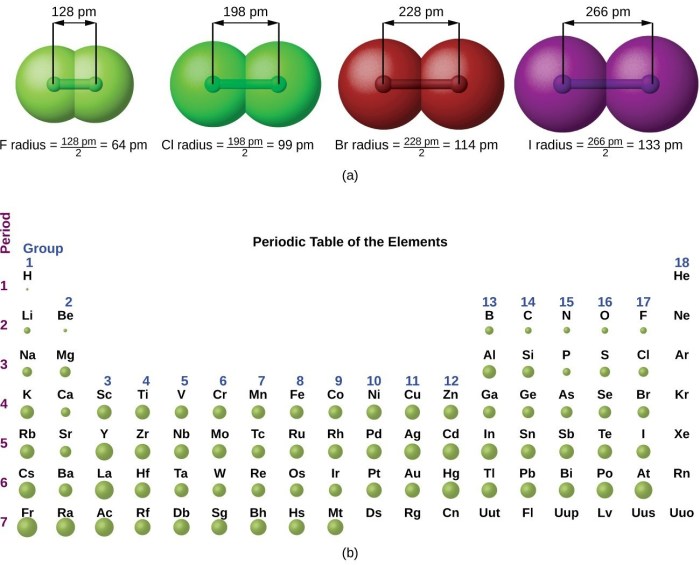
Atomic radius refers to the distance from the nucleus of an atom to its outermost electron shell. It is a fundamental property that determines the size and reactivity of an atom. Atomic radius exhibits a periodic trend across the periodic table, providing valuable insights into the behavior of elements.
Methods for Determining Atomic Radius
Experimental methods play a crucial role in determining atomic radii. These include:
- X-ray crystallography:Involves analyzing the diffraction of X-rays by crystals to determine the positions of atoms and their radii.
- Electron diffraction:Uses the diffraction of electrons by gases to determine the atomic radii of gaseous elements.
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy:Measures the magnetic resonance frequencies of atomic nuclei to provide information about atomic radii.
Factors Affecting Atomic Radius: Arrange These Elements According To Atomic Radius
Atomic radius is primarily influenced by the following factors:
- Atomic number (Z):As Z increases, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, attracting more electrons and reducing the atomic radius.
- Electron configuration:Atoms with more electrons in higher energy levels have larger atomic radii due to increased electron-electron repulsion.
- Shielding effect:Inner electrons shield the outer electrons from the nucleus, reducing the effective nuclear charge and increasing the atomic radius.
Trends in Atomic Radius Across the Periodic Table
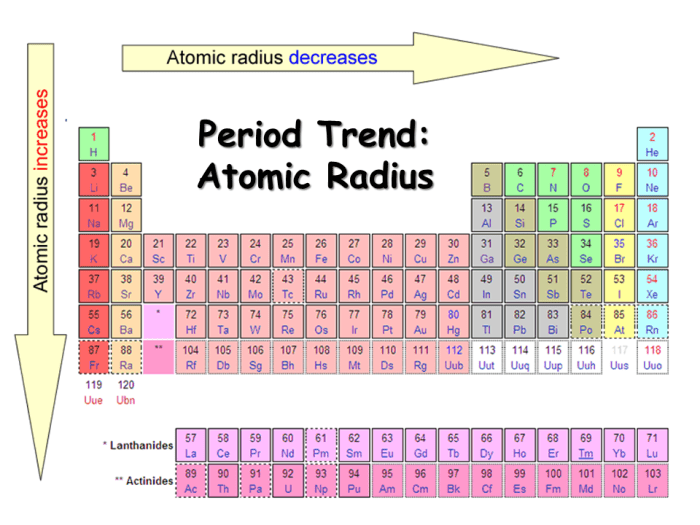
Atomic radius exhibits distinct trends across the periodic table:
- Across a period (left to right):Atomic radius generally decreases as the atomic number increases, due to the increased nuclear charge and reduced shielding effect.
- Down a group (top to bottom):Atomic radius increases as the atomic number increases, due to the addition of new energy levels and increased shielding effect.
| Group | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period 2 | H | He | ||||||
| Period 3 | Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne |
| Period 4 | Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar |
| Period 5 | K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe |
Applications of Atomic Radius
Atomic radius plays a crucial role in predicting chemical properties:
- Ionic radii:Atomic radii can be used to estimate the size of ions, which is important for understanding ionic bonding and crystal structures.
- Covalent radii:Atomic radii can be used to predict the bond lengths of covalent compounds, providing insights into molecular geometry and reactivity.
- Metallic radii:Atomic radii can be used to determine the packing of atoms in metals and predict their physical properties.
FAQ Explained
What is atomic radius?
Atomic radius refers to the distance from the nucleus of an atom to its outermost electron shell.
How is atomic radius determined?
Experimental techniques such as X-ray crystallography and electron diffraction are used to measure atomic radius.
What factors affect atomic radius?
Atomic radius is influenced by atomic number, electron configuration, and shielding effect.