w varies directly with u and inversely with d, an intriguing concept in mathematics, unveils a captivating interplay between variables. Direct variation implies a proportional relationship where w increases or decreases in tandem with u. Inverse variation, on the other hand, suggests an inverse proportionality, where w and d move in opposite directions.
This intricate relationship between w, u, and d unfolds in a series of equations and real-world examples, providing a deeper understanding of the concept and its practical applications.
Direct and Inverse Variation

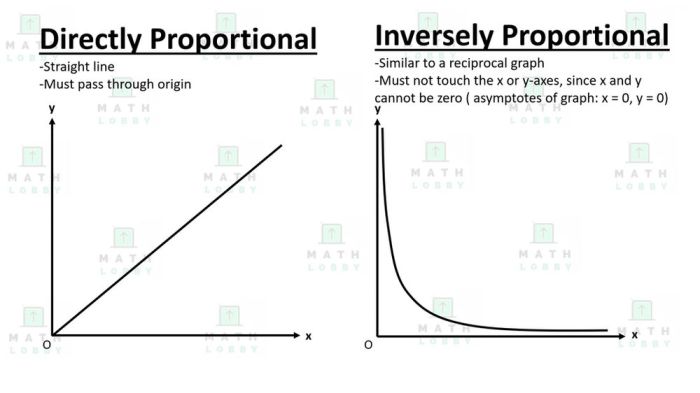
In mathematics, variation describes how one variable changes in relation to another variable. Direct variation occurs when one variable increases or decreases in the same proportion as another variable, while inverse variation occurs when one variable increases or decreases in inverse proportion to another variable.
The given statement, “w varies directly with u and inversely with d,” indicates that the variable w is directly proportional to u and inversely proportional to d.
Direct Variation with u
Direct variation is a relationship between two variables where one variable increases or decreases in the same proportion as the other variable. The equation representing direct variation is:
w = ku
where w is the dependent variable, u is the independent variable, and k is the constant of variation.
In this case, w varies directly with u, which means that as u increases, w also increases, and as u decreases, w also decreases. The constant of variation, k, determines the specific rate of change between w and u.
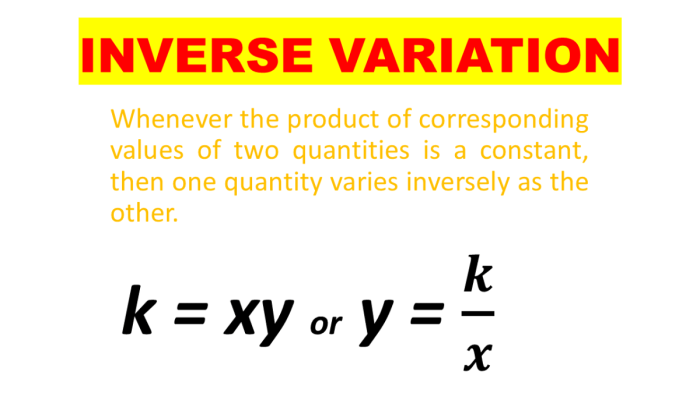
Inverse Variation with d
Inverse variation is a relationship between two variables where one variable increases or decreases in inverse proportion to the other variable. The equation representing inverse variation is:
w = k/d
where w is the dependent variable, d is the independent variable, and k is the constant of variation.
In this case, w varies inversely with d, which means that as d increases, w decreases, and as d decreases, w increases. The constant of variation, k, determines the specific rate of change between w and d.
Combined Variation
The given statement combines direct variation with u and inverse variation with d. To represent this combined variation, we can combine the two equations:
w = k(u/d)
This equation shows that w varies directly with u and inversely with d. As u increases, w increases, and as d increases, w decreases. The constant of variation, k, determines the specific relationship between w, u, and d.
The following table illustrates the combined variation:
| u | d | w |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 2k |
| 4 | 1 | 4k |
| 2 | 2 | k |
| 4 | 2 | 2k |
The table shows that as u increases, w increases, and as d increases, w decreases. This demonstrates the combined variation of w with u and d.
Examples
Here are some real-world examples where w varies directly with u and inversely with d:
- The force of friction (w) varies directly with the coefficient of friction (u) and inversely with the normal force (d) applied to the surfaces in contact.
- The amount of light intensity (w) varies directly with the distance from the light source (u) and inversely with the square of the distance (d) from the light source.
- The speed of a moving object (w) varies directly with the applied force (u) and inversely with the mass of the object (d).
These examples demonstrate the concept of combined variation, where one variable varies directly with another variable and inversely with a third variable.
Applications, W varies directly with u and inversely with d
The concept of combined variation has practical applications in various fields:
- In physics, it is used to calculate forces, velocities, and other physical quantities.
- In engineering, it is used to design structures and machines that can withstand varying loads and conditions.
- In economics, it is used to model supply and demand, pricing, and other economic factors.
By understanding the principles of combined variation, we can better analyze and predict the behavior of complex systems in various disciplines.
Quick FAQs: W Varies Directly With U And Inversely With D
What is direct variation?
Direct variation refers to a proportional relationship between two variables, where one variable increases or decreases in direct proportion to the other.
How is inverse variation different from direct variation?
Inverse variation describes a relationship where one variable increases as the other decreases, and vice versa.
What is combined variation?
Combined variation combines both direct and inverse variation, allowing us to analyze the relationship between a variable and multiple other variables simultaneously.