Fossil evidence of evolution worksheet – Delve into the captivating realm of fossil evidence of evolution, where ancient relics whisper tales of life’s extraordinary journey. This comprehensive worksheet unravels the significance of fossils in deciphering the history of life on Earth, offering a glimpse into the mechanisms that have shaped the diversity of species we witness today.
As we embark on this exploration, we will delve into the diverse types of fossil evidence, unravel the methods employed to analyze these remnants, and uncover compelling examples that illuminate the gradual transformations of species over eons. Along the way, we will acknowledge the challenges inherent in interpreting fossil evidence, ensuring a nuanced understanding of this invaluable scientific tool.
1. Define Fossil Evidence of Evolution

Fossil evidence of evolution refers to the preserved remains or traces of organisms that existed in the past. These fossils provide valuable insights into the history of life on Earth and the evolutionary relationships between different species.
2. Types of Fossil Evidence: Fossil Evidence Of Evolution Worksheet
Body Fossils
Body fossils are the preserved remains of organisms, such as bones, shells, and teeth. They provide direct evidence of the organism’s morphology and can be used to study its anatomy, behavior, and ecology.
Trace Fossils
Trace fossils are evidence of an organism’s activity, such as footprints, burrows, and nests. They provide insights into the behavior and habitat of the organism, as well as the environmental conditions in which it lived.
Chemical Fossils
Chemical fossils are the preserved chemical remains of organisms, such as lipids, proteins, and DNA. They can provide information about the organism’s biochemistry, diet, and environment.
3. Methods of Analyzing Fossil Evidence

Comparative Anatomy
Comparative anatomy compares the anatomical structures of different organisms to identify similarities and differences. These comparisons can provide insights into evolutionary relationships and the common ancestry of species.
Paleontology
Paleontology is the study of fossils and the history of life on Earth. Paleontologists use fossils to reconstruct past environments, understand the evolution of species, and investigate the causes of extinction.
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is the study of the layering of rock formations. It helps determine the relative ages of fossils and provides a chronological framework for understanding the history of life on Earth.
4. Examples of Fossil Evidence Supporting Evolution
Transitional Fossils
Transitional fossils are fossils that show intermediate characteristics between two different groups of organisms. For example, Archaeopteryxis a transitional fossil between reptiles and birds.
Homologous Structures
Homologous structures are structures in different organisms that have similar underlying structures and developmental origins, indicating a common ancestry. For example, the forelimbs of humans, bats, and whales are homologous structures.
Molecular Evidence
Molecular evidence, such as DNA and protein sequences, can provide insights into the evolutionary relationships between organisms. By comparing genetic sequences, scientists can determine the degree of relatedness between species and reconstruct their evolutionary history.
5. Challenges to Interpreting Fossil Evidence

Incompleteness of the Fossil Record, Fossil evidence of evolution worksheet
The fossil record is incomplete due to factors such as taphonomy (the processes that lead to the preservation of fossils) and the limited preservation potential of soft tissues. This incompleteness can make it difficult to reconstruct the full evolutionary history of organisms.
Bias in Fossil Discovery
Fossil discovery is often biased towards certain types of organisms and environments. For example, marine fossils are more likely to be preserved than terrestrial fossils. This bias can affect our understanding of the diversity and evolution of life on Earth.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of fossil evidence in understanding evolution?
Fossil evidence provides direct physical evidence of past life forms, allowing scientists to trace the changes in species over time and reconstruct the history of life on Earth.
How do scientists analyze fossil evidence?
Scientists use comparative anatomy, paleontology, and stratigraphy to analyze fossil evidence, comparing anatomical structures, studying the fossil record, and examining the geological context of fossils to infer evolutionary relationships.
What are some examples of fossil evidence that support the theory of evolution?
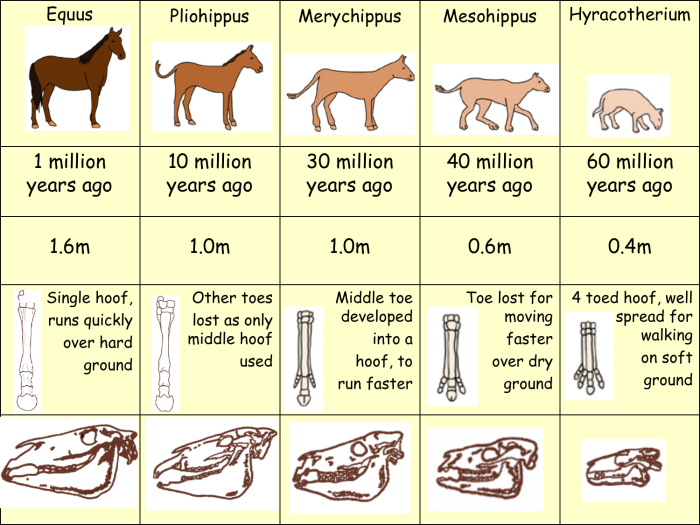
Examples include transitional fossils, such as Archaeopteryx, which exhibit characteristics of both reptiles and birds, and the fossil record of horse evolution, which demonstrates the gradual changes in body size, limb structure, and tooth morphology over millions of years.